Arable Farming In India : Important Verticals Clarified

Arable agriculture in farming has been the primary source of commerce in India. In fact, arable farming still employs the major part of the Indian labour force. There are many reasons for such conditions in the southeastern subcontinent, such as poverty, lack of agricultural diversity, lack of investment capital, and lack of awareness among farmers. But, most importantly, the growing population in the subcontinent have demanded major revolutions to feed the country with time. One such awakening was the Green Revolution.
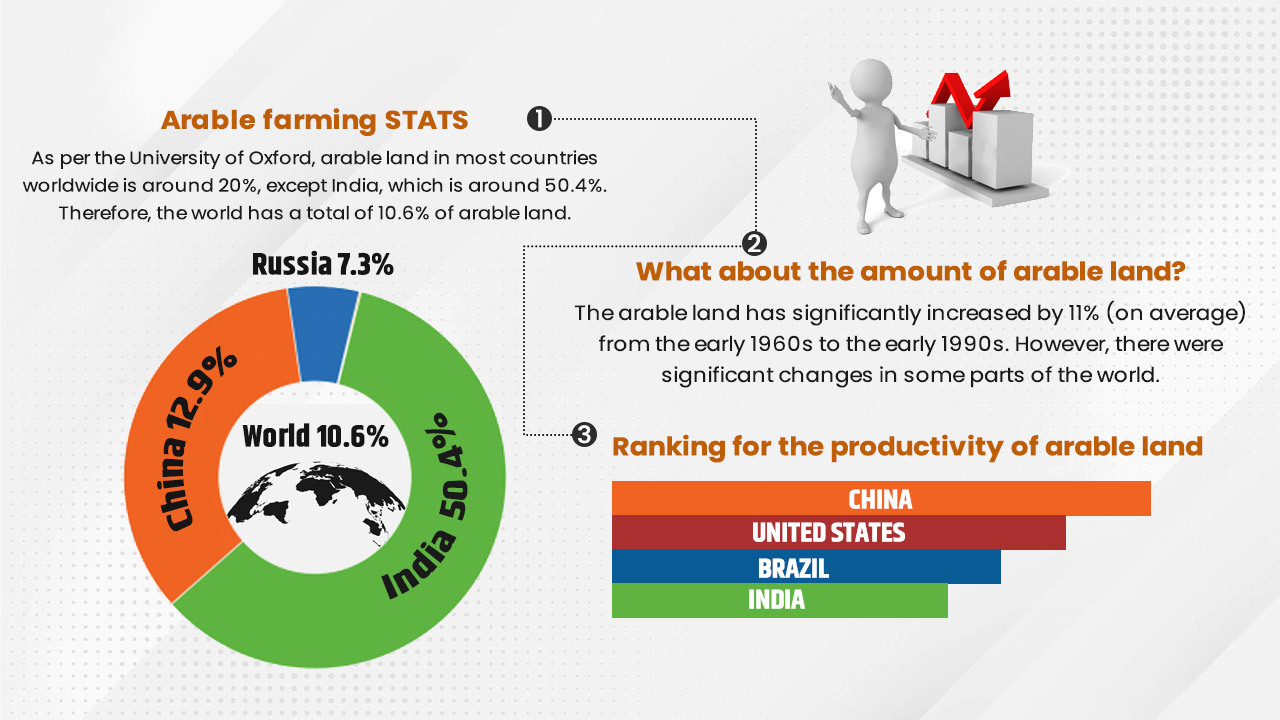
According to a survey conducted by Wikipedia, India ranks at the top of the chart in the case of arable land present on its soil, with a score of 50.4%. This percentage tells the importance of arable farming and its related agriculture. In this blog, we will discuss several verticals of arable farming in India and the rest of the world.
Process and meaning of arable farming with example
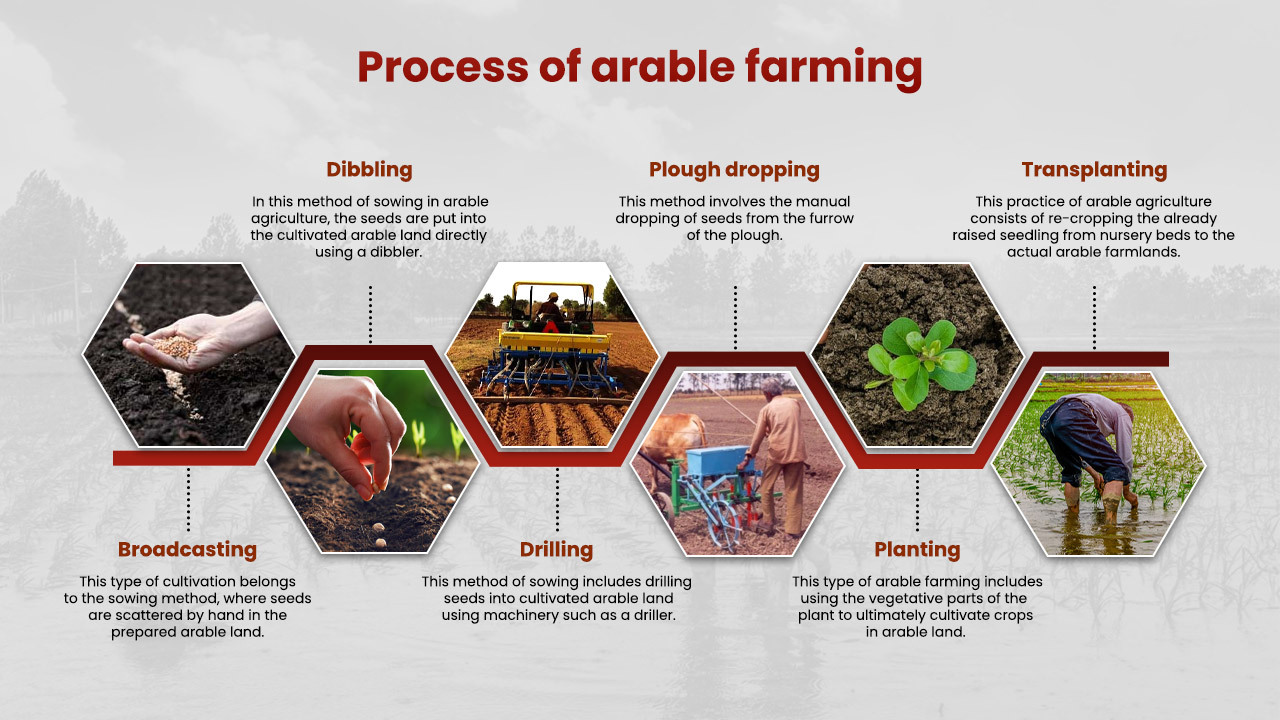
Process
Arable farming involves two processes, i.e. planting and sowing. Let us discuss and understand these two before moving forward.
1. Sowing: Arable farming in which the seed is directly put into the soil.
2. Planting: Live plants are directly put into the soil in this type.
The above two processes mainly define arable agriculture in detail. Furthermore, in this type of farming, the following processes of sowing and planting are steps for the cultivation of staple crops.
- Broadcasting: This type of cultivation belongs to the sowing method, where seeds are scattered by hand in the prepared arable land.
- Dibbling: In this method of sowing in arable agriculture, the seeds are put into the cultivated arable land directly using a dibbler.
- Drilling: This method of sowing includes drilling seeds into cultivated arable land using machinery such as a driller.
- Plough dropping: This method involves the manual dropping of seeds from the furrow of the plough.
- Planting: This type of arable farming includes using the vegetative parts of the plant to ultimately cultivate crops in arable land.
- Transplanting: This practice of arable agriculture consists of re-cropping the already raised seedling from nursery beds to the actual arable farmlands.
Meaning of Arable Farming
Arable agriculture is the type of farming that encourages land preparation as per the crop requirements for organized crop cultivation and harvesting. It includes the production of staple crops such as wheat, rice, maize, etc., on a large, medium or small scale.
History of Arable Farming
Arable land originated from the Latin word Arabilis, meaning able to be ploughed. Henceforth, any arable land on which planned agriculture takes place comes in the arable farming category. Arable farming began when humans lived in less nomadic societies, i.e. 11000 years ago. The era that belonged to the particular time frame was called the Paleolithic period. After the end of this era, nomadic humans became more organized and started practising arable farming system.
Importance of Arable Agriculture in Farming
Arable farming was discovered as humans felt the necessity of organized farming. Be it any time frame, arable agriculture is solely responsible for producing food crops to fulfil human needs. Furthermore, the core livestock population depends on arable agriculture and its practices. In addition to all these factors, arable farming has fulfilled human food and animal fodder needs. As the demand for food rises with population growth, only arable farming has the potential to fulfil the demand.
Arable Crop Production : List of Arable Crops

Arable crop production is responsible for producing an ample range of annual, half-yearly, and quarterly crops. Hence depending on the type of consumption among humans and livestock, arable crops are divided into the following types :-
- Grain crops: Crops such as wheat, maize, rice, barley, etc.
- Pulse crops: These are edible legumes that restore nitrogen into the soil. For example, lentils, beans, and peas.
- Oilseed crops: These crops yield oil through their seeds. Examples are rapeseed, soybean, etc.
- Forage crops: Animals eat these crops as fodder. For example, cowpea, clovers and timothy.
- Fibre crops: Arable land grows crops for taking out clothing and non-clothing fibres from the plant. E.g. cotton, jute, flax
- Tuber crops: These types of arable crops have their edible parts buried under the ground.
Arable Farming : The Types
Arable Farming technology has grown and developed over the years. This led to different practices/types of arable farming for soil sustainability and land equality. Below are the mentioned derivates of the arable farming system out of time.
Organic Arable Farming
This type of arable farming system includes organic practices of agriculture which uses only carbon and carbon derivatives as fertilizers, nitrogen fixtures, pesticides and insecticides. In this method soil restoration takes place. Although the process is a bit expensive in the modern era, a lesser part of arable land influences organic arable farming. But, the method has a long-lasting effect on the characteristics of arable farming land.
Intensive/Inorganic arable farming
Intensive or inorganic farming includes every method (except organic) employed to increase crop production without caring about the soil’s natural fertility. Or in other words, the sustainability of arable land is compromised. Due to intensive arable farming, humans have exploited a lot of arable lands. Due to this factor, intensive/inorganic arable farming is now is demoted for sustainability reasons.
Arable Farming and its Commerce
Arable farming in India mainly commercialises crops, as agriculture is the backbone of the Indian economy. India stands tall when it comes to arable farming and its culture. In addition, arable agriculture in India is solely responsible for feeding the largest livestock and second-largest human population in the world. Therefore, arable farming in India has different mottos to fulfil.
Use of Technology in Arable Farming
Nowadays, technology has revolutionalized, synchronized, and empowered almost every farming sector. The following technologies have brought revolutionary changes in arable farming.
- Drones (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles): This technology uses apt sensors. for crop monitoring, crop care, nutrient management, etc.,
- IOT (Internet of Things): This technology uses furnished data to calculate and thus easily predict information useful for arable farming.
- Machine learning: This technology uses consistent learning of data processing and thus outputs informed data for farmers involved in arable farming.
- Artificial Intelligence: In this technology, the computing device uses their own intelligence to learn and henceforth predict arable farming enhancement possibilities. This, in turn, has revolutionized arable agriculture in farming.
The final thought
In this blog, we discussed arable farming and its different verticals. Henceforth, we came to a common conclusion that sustainable, tech-driven and eco-friendly arable farming can only feed the growing population of India and the rest of the world. Furthermore, we also promote organic arable farming as it is the only way to optimize the productivity of the soil. So, go arable, go green, go sustainable.
At Tractorguru, we analyse, inform, and awaken farmers across nations by providing them with correct agricultural and agri-machinery information. Do join and follow our channel at Google news.
Related Blogs:



