Rabi and Kharif Season – Farmers Friendly Seasons for Cultivation in India

Rabi season and Kharif season are the seasons, in which mostly crops are cultivated in India. Around 100% of farmers cultivate the crops during these seasons but the counting of farmers who cultivate the crops during the third season is less. That’s why we can say that the farming business is more dependent on these two popular Rabi and Kharif season.
Kharif Season
Those crops that thrive during the rainy season are mainly called the Kharif crop. Kharif season begins from the start of the monsoon. The kharif season month starts from June and remains last upto November.
Rabi Season
Rabi season crops are grown in starts from October after the end of the monsoon and stays till last April. Therefore, many farmers grow Rabi crops due to adequate water availability with soil moisture in the Rabi Crop Season. Rabi crop farming requires a warm climate for seed fertilisation and a cold climate for the better and effective growth of crops.
What is the kharif Season Crop?

Kharif crops, also called the monsoon crops or autumn crops, are considered domestic plants cultivated and harvested in India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh. It thrives according to the Indian subcontinent’s monsoon season, which lasts from June to November, depending on the area’s climate.
According to the Indian subcontinent’s monsoon season, it may begin in early May. However, the Kharif crops are generally harvested from the third week of September to October.
Kharif crops examples are Rice, maize, and cotton are some of the significant Kharif crops in India.
What are Rabi Crop Season?

Rabi crops are planted between October and November. Therefore, Rabi crop farming requires a low temperature at the time of planting the crop. Same as well, rabi crops are harvested in the months where a dry or warm environment is needed. Therefore, the season of rabi crops requires less moisture and a cool environment to grow. The Rabi crops are grown with rainwater that has filtered into the ground. Rabi harvest time is also needed for a perfect climate to harvest.
Example of rabi crops in India are wheat, barley, mustard, sesame, peas and many more.
Crops Grown in the Kharif Season And Rabi Season
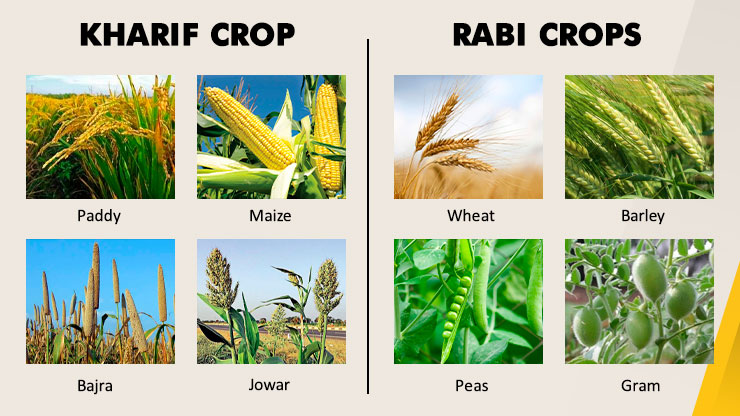
|
Types of Kharif Crop Crops grown in the Kharif season are Paddy, Maize, Bajra, Jowar, Soybean, Castor, Cotton, Sugarcane, Turmeric, Guar, Turmeric, Ragi. Some Kharif vegetables are Chilly, Bitter gourd, Okra, Brinjal and many more. |
Types of Rabi Crops Popular crops grown in Rabi season are Wheat, Barley, Peas, Gram and Mustard. A rabi crop that is also one of the Pulses, Oats, Linseed and many more. |
Difference Between Rabi Crops And Kharif Crops
|
Basis |
Rabi Crops |
Kharif Crops |
| Cultivation Season | Rabi Crops are planted around the Retreating Monsoon and Northeast monsoon season, which starts from October and is also called rabi or winter crops. | Kharif Crops are sown during the monsoon season and it is also called monsoon crops. |
| Harvesting Season | The harvest for Rabi crops happens during April and May, in the summer season. | Kharif Crops are planted at the starting of the season, end of May or early June, and Kharif crops are harvested after the monsoon or starting October. |
| Rainfall Requirement | The rainfall does not much influence rabi crops. | All Kharif crops depend on rainfall. |
| Crops | Major Rabi crops considered wheat, gram, peas, barley etc. | Kharif crops are considered many crops: rice, maize, pulses such as urad, moong dal, millets, and many more. |
| Climate | A hot climate is essential for Rabi crop seed germination and a cold climate for the better growth of rabi crops. | It requires so much water and a warm climate to thrive. |
Cultivation Process of Kharif Crop

1. Rice Cultivation
Rice is one of the essential food crops of India. A significant share of rice grows during the Kharif season. But a small portion of rice produces in the rabi /summer season with specific irrigation. Therefore, rice production mainly depends on the monsoon and rains in India.
-
How to grow Rice?
Conditions of Rice growth
The temperature should be around 24°C a month. It must be approximately 20°- 22°C at the time of planting, 23°-25°C should be at the time of growth, 25°-30°C should be at the time of harvesting. The annual rainfall required for rice is approximately 150 cm.
-
Methods of Rice Farming
Broadcasting Method
Seeds are planted and scattered by hands. This method is followed in those areas which are relatively dry and less productive. So, it is the easiest method that requires minimum input, but its production is also minimum.
Drilling Method
This process considered the ploughing of land and planting the seeds. This drilling method is mainly defined in pan India.
Transplantation Method
This transplantation method is followed in the areas of rich soil, ample rainfall and a sufficient supply of labour.
Japanese Method
This method includes using broad productive seeds, planting the seeds in a raised nursery-bed. Then, it transplants the saplings in rows to make weeding and preparing easy. This Japanese method of rice farming is favourably used in the mostly rice-producing regions of India.
2. Maize Cultivation
Maize is a very important and Kharif season crop and food as well with green forage. It is popularly known as “Queen Of The Cereals”. It has the highest production per hectare with the cereal crops.
Climate Condition
Maximum temperature for germination is 21°C and for better growth is 32°C respectively.
Harvesting
Maize matures within 90-110 days. This plant may remain green when cobs of maize are dry & ready for harvest.
3. Cotton Cultivation
The cotton crop is usually raises in medium to deep black clayey soil. But it can also grow in sandy and loam soil through irrigation. Therefore, cotton can grow in both under-watered and rainfed conditions.
Cotton is a popular Kharif crop in significant Indian states like Punjab, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Haryana, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh. In these areas, the irrigated crop plants from March-May. The rain-fed crop grown in June-July with the start of the monsoon.
In this cultivation process, one thing is still the same, the farm vehicle. Without a best farm vehicle, especially a tractor, any farmer cannot start farming. For better farming assistance, here we are recommending you the VST tractor and VST implements also.
Cultivation Process of Rabi Crop

1. Mustard Cultivation
Mustard is popularly grown in Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, UP, Haryana, Gujarat. Also, some areas of the south like Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu. Yellow Sarson is also known as a rabi crop in Assam, Bihar, Orissa and West Bengal.
Soil Requirement
- Light to heavy soil is proper for mustard and rapeseed cultivation.
- Raya mustard variety can be grown in all soil types, whereas loam and heavy soils are suitable for toria crops.
- And Sandy and loamy sand soils are suitable for a variety of Taramira mustard crops.
Land Preparation
- Fine seedbeds are required for the excellent germination of crops.
- It would be best if you do ploughing of soil two to three times followed by two harrowings.
- It would be best if you do planking after every ploughing.
Planting
- The time for planting Mustard crops starts from September to October.
- For the toria crop, planting begins from the first fortnight of September to October.
- For African sarson and Taramira can be sow in the whole October month.
- The Raya mustard crop is completely plants from Mid of October to November End.
Harvesting
- Depending on the variety, the mustard crop takes 110 to 140 days to mature.
- If you see the seeds turn yellow and become stiff, then harvest the crop.
- It would be best if you cut crops close to the ground with the help of a sickle.
- Pile the stored crops for 7-10 days.
- Then complete the separating operation after proper drying.
2. Wheat Cultivation
Wheat is a main grain crop in India. The total area covered under the crop is around 29.8 million hectares in the country.
Choosing a good location is an essential part of wheat farming is the selection of an appropriate place. For that, you should look for a place with fertile soil for wheat farming.
Soil Preparation
Soil preparation properly starts before wheat farming. For this, you can turn the soil either with a disc or mouldboard. After that, arrange the soil by giving one deep plough, with 2 to 3 light ploughing and planking.
Weather
The perfect climate for wheat farming is misty and cool weather, possible in the Rabi season. The plants can easily grow and survive in temperatures which start between 3.5 °C and 35 °C. The best temperature for wheat farming starts from between 21 °C and 26 °C.
Harvesting
Harvesting starts when the leaves and stems turn yellow and become relatively dry. Then the wheat’s moisture content reaches about 25 – 30%, then the wheat is ready to be harvested.
3. Peas Cultivation
Pea is planted worldwide, and in India, you can find it in many Indian states like Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, West Bengal, Orissa and many more.
Climate
For pea farming, the temperature should range between 15 degrees to 30 degrees Celsius. The maximum rainfall range should be between 400 to 500 mm.
Soil Requirements
You can do pea farming on several soil types. However, peas cultivation cannot grow in waterlogged areas.
Harvesting
Start harvesting peas between 45 to 60 days. Start the midseason and the late-season crop between 75 days and within 100 days.
Whether it is a rabi season or kharif season, the farming vehicle remains the same. The tractor cannot be replace in the farms to plough from any other vehicle. If you are going to buy a perfect, reliable and robust farming tractor, you should check Kubota tractor for once.
We hope you find this content relevant and knowledgeable about Rabi and Kharif season. For more information about rabi crop and kharif crop, stay connected with TractorGuru.
Related Blog:



