Sugarcane Cultivation in India – How to Cultivate Sugarcane

Sugarcane belongs to the bamboo family and is indigenous to India. It is the main source of jaggery, sugar and Khansari. In India, around two-thirds of the total sugarcane production is consumed for making Khansari and jaggery, and only one-third is used for the production of sugar from sugarcane. It also offers raw materials for manufacturing alcohol. Brazil is the largest producer of sugarcane, after that India, China, Pakistan, Thailand, Mexico etc. Moreover, Maharashtra is the largest producer of sugarcane in the subtropical region in India. In the below section we are describing the process of sugarcane cultivation.
Important Zones/ Regions for Sugarcane Production
There are two distinct agro-climatic zones of sugarcane cultivation in India, namely tropical and sub-tropical. However, five climatic zones have been identified to cultivate sugarcane varieties. They are 1. North Central Region 2. North Western Region 3. Coastal Region 4. North Eastern Region 5. Peninsular Region.
Sugarcane Cultivation Process in India

There is the complete information regarding; how is sugarcane cultivated.
Climatic Condition for Sugarcane Cultivation
Sugarcane is known as a tropical plant, and also it is a long duration crop. Thus, it encounters all the seasons, viz., rainy, winter, rainy and summer, during its life cycle. The sugarcane plant thrives best in warm tropical areas. In a long, hot growing season with a high incidence of ample moisture (rainfall) and solar radiation – the plant uses 148 to 300 grams of water to produce 1.0 grams of dry matter. Simply, you should also follow this chart to produce the highest yield.
|
Temperature 20-30°C |
Sowing Temperature 20-25°C |
Irrigation 75-150cm |
Harvesting Temperature 20-30°C |
Soil Requirement for Sugarcane Crop Production
Well-drained, loamy deep soil with a groundwater 1.5-2 m below the soil surface with ample water holding capacity is the best for sugarcane cultivation. It can tolerate acidity and alkalinity to a large extent, so it can be grown on soils ranging from 5 to 8.5. If the soil pH is low (less than 5), add lime to the soil and for high pH (greater than 9.5), apply gypsum.
Land Preparation for Sugarcane Plant
Take land for two ploughings and first ploughing is done at a depth of 20-25 cm. Then, crush the clouds with suitable tools or machines. However, on average, 40 to 50 quintals of sugarcane production per acre of land. Some other objective is to prepare the land for sugarcane cultivation.
- Creating a seedbed that allows optimum soil water air relations
- Good physical condition for early root penetration and also for propagation
- Incorporation of pre-harvest residues and organic manures
- To destroy hibernate and weeds pest and disease organisms
- To facilitate proper soil chemical and microbial activity
How to Sow the Seeds of Sugarcane

1. Sowing Time
The sowing season of sugarcane is from September to October and February to March. Sugarcane generally takes one year to mature; hence it is called ekalali.
2. Spacing and Sowing Depth
For subtropical areas, you should keep the row spacing ranging from 60 cm to 120 cm. Sow the seeds of sugarcane at a depth of 3-4 cm, and also you should cover it with soil.
3. Sugarcane Cultivation Methods of Sowing
A. Dry Planting in Furrow and Ridges
You can make the furrow and ridges 90 cm apart with the help of a tractor-drawn ridge. Then, plant the sets of sugarcane and cover them with soil. After that, you need light irrigation.
B. Paired Row Planting
Make trenches at a distance of 150 cm using a trench opener. Plant sugarcane crop in a pair using 30:30-90-30:30cm spacing. It gives a higher yield than weeds and furrows.
C. Ring Pit Method of Sugarcane Cultivation
With a tractor-mounted digger, circular pits of a diameter of 60 cm are dug at a depth of 30 cm. A gap of 60 cm is provided between adjacent pits. As a result, you can obtain a 25-50% higher yield than ridge and furrow and ridge.
How to Care for a Sugarcane Plant?
A. Weed Control
About 12 to 72% yield loss is observed in sugarcane, depending on the severity of weed infestation. Therefore, you should adopt weed management practices 3 to 4 months after planting. Chemicals are not the only solution for weed control. Therefore, adopting these methods to provide an effective solution for sugarcane crop cultivation.
1. Mechanical Measure: Since sugarcane is a widely spaced crop, hand weeding or intercultural operations can be done easily. Do 3-4 weddings after every irrigation.
2. Cultural Operations: It included a change in trash mulching, cropping pattern and also difference in intercropping.
3. Chemical: To control weeds, carry out pre-emergence weedicide application with Atrazine@600-800 g/acre or Diuron@1- 1.2 kg/acre or Metribuzine@ 800 g/acre.
B. Fertiliser Dose Requirement
After every three years, a soil test is necessary to know the actual fertiliser requirement. Before sowing at the time of the last ploughing, apply well-decomposed cow dung @ 8 tonnes or Vermicompost + Rallygold @ 8-10 kg or PSB @ 5-10 kg per acre.
Apply Urea at 66 kg/acre at the time of sowing. Then, apply a second dose of 66 kg urea at the time of the second irrigation in the growth stage. Finally, apply the third dose of 66 kg urea at the time of the fourth irrigation.
C. Pest and Their Control
Early shoot borer: The internodes invade the structures in the germination stage.
Avoid late sowing and with the help of rose, apply Chlorpyrifos @ 1 litre per acre mixed with 100-150 litres of water on the troughs.
White Grub: These feed on the root system and thus damage the crop.
Do not delay the sowing of the crop. Treat sugarcane with Chlorpyrifos before sowing. Apply Carbofuran @ 13 kg or Phorate @ 4 kg per acre to the soil at sowing or before.
D. Disease and Their Control
Red Rot: From above, the third and fourth leaves appear yellow and dry.
To control the growth of disease-resistant varieties. Select disease-free sugarcane for sowing.
Pokkah Boeng: It is an airborne disease, and you can observe the symptoms in monsoon.
If you observe infection of the disease, spray with Copper Oxychloride@3gm/Ltr or Carbendazim@4gm/Ltr or Mancozeb@3gm/Ltr of water.
Harvesting
Harvesting sugarcane at an early age or a young age leads to a loss in sugarcane yield. Also, you can decide the harvesting time based on the wilting of leaves. Some farmers use hand sugar refractometers to know the exact time of harvesting also a sickle is used for harvesting. The stalks are cut at ground level to cut off the sugar-rich internodes below that connect the stems and sugar—De-topping at the proper height. The post-harvest sugarcane needs to be promptly disposed of in the factory.
Byproducts of Sugarcane
A. Fuel & Chemical
Ethanol – This production from sugarcane starts when cane stalks are crushed to extract a sugar-rich cane juice. According to the market research, the cost of ethanol production from sugarcane juice has been around Rs 63.45 per litre.
Biogas – The process of biogas production from sugarcane bagasse is a well-known organic residue widely generated from sugar mill factories.
B. Fibre
Cellulose – It covers about a third of the sugarcane plant tissue. Sugarcane bagasse contains approximately 25-35% hemicellulose and 40-50% cellulose .
C. Food
Jaggery and Syrup- Jaggery and syrup are a non-traditional sweetener made by boiling sugarcane juice.
D. Fodder
Sugarcane can be used as green fodder and provide valuable dry season fodder.
Interesting Facts about Sugarcane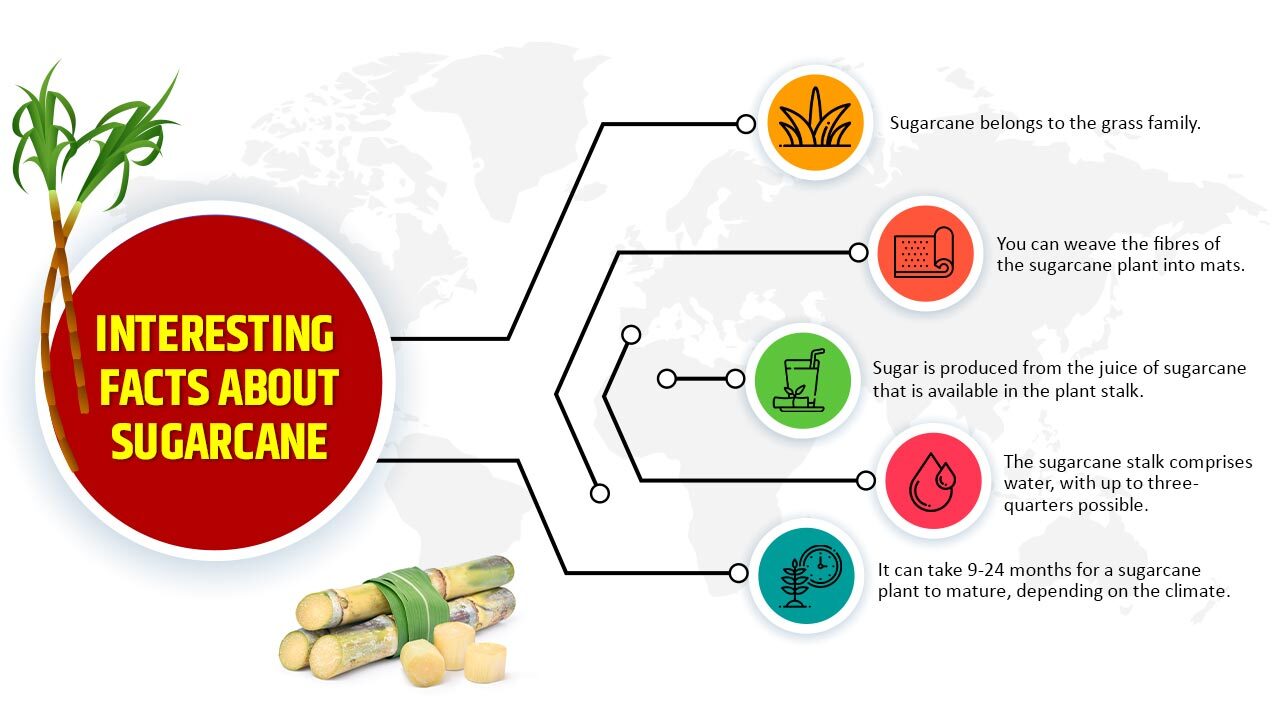
For further information regarding alcohol production from sugarcane, byproducts of sugarcane processing, SSI method of sugarcane cultivation, global sugarcane production and organic sugarcane cultivation, stay tuned with TractorGuru.
FAQS
Que. Which is the most cultivated species of sugarcane?
Ans. Saccharum officinarum is one of the most productive and most intensively cultivated kinds of sugarcane.
Que. What is the best production technology of sugarcane?
Ans. Especially during the dry season, sugarcane growers use technology to fight fires, such as using NASA satellites for real-time monitoring of fire outbreaks.
Que. How many byproducts of sugarcane industry?
Ans. Sugarcane industry has four main byproducts such as bagasse, cane tops, filter muds and molasses.
Que. How much does the cultivation of sugarcane cost?
Ans. The overall cost of cultivation of sugarcane is around Rs 87491.30 per hectare.
Que. Where is the highest production of sugarcane in India?
Ans. Uttar Pradesh is the most extensive sugarcane producing state in the subtropical region, with 135.64 million tonnes of production.
Que. How much sugarcane productivity in India?
Ans. The sugarcane yield produced across India is approximately 82 metric tons per hectare.
Que. Which is India’s rank in sugarcane production?
Ans. India ranks 2nd in sugarcane production.
Related Posts:



